Ransomware threats have proved a real-time threat for the computer users for quite some time now. They attack your systems and hold it for ransom. Though these threats were originated in the late 80s, they still have momentum in the new millennium. In fact, criminals are building a new industry based on these malicious programs. Decryption of these programs take time thus attackers manage to make a fortune using this technique. They use their malicious programs to target both, personal users and corporates.
Let’s decode the ransomware threat to understand it in a better way.
Decode Ransomware Threat:
What is ransomware?
Ransomware is a computer malware designed to harm victim’s computer by encrypting files or locking the system’s screen. Ransomware attackers use Cryptovirology to design the powerful malicious software. It is designed to deny access to the victim’s system and further it demands a ransom to allow access to the system. They target users in web-based and email based formats.
Ransomware model:
The model of ransomware works upon malicious activities initiated by the criminals. They create a malicious program using their expertise to lock down your system and then ask for a ransom. They drop a malicious code via emails or links and ask you to open it. It is also spread through spam campaigns and compromised websites. The damaged caused by the program varies according to the coding of the ransomware program. It can affect your system by locking it down by encrypting your files or it can attack your system’s Master File Table (MFT) or entire hard disk. Decrypting these vigorous programs becomes a tough job even for experts from the industry. Decryption key to most of these ransomware programs is still unavailable.
Few biggest ransomware attacks of recent times:
Locky ransomware:

As the name suggests, this ransomware was designed to lock you out from your system. This ransomware encrypts your files and changes their extension to “.locky”. It attacks users through spam email campaigns, many of which are disguised as invoices using subject lines such as “ATTN: Invoice J-[RANDOM NUMBERS]” and “tracking documents”. It encrypts files with a strong RSA-2048 + AES 128 ciphers. Once it encrypts your files it demands a ransom of 0.5 bitcoin to 1.00 bitcoin. Researchers are working to decrypt .locky files.
Petya ransomware:

Petya attacks the victim’s computer in a different way. Instead of encrypting files one by one, it denies access to the whole system. It attacks the low-level structure on the disk. It drops malicious code via spam emails posing as a job application. It contains a link to an online storage service and an executable PDF document (malicious). Petya ransomware replaces computer’s Master Boot Record with its own malicious boot loader. Next, it encrypts computer’s Master file table (MFT) which makes system unable to boot. Petya Ransomware requires administrator privileges to further run the next malicious code.
CryptoLocker:
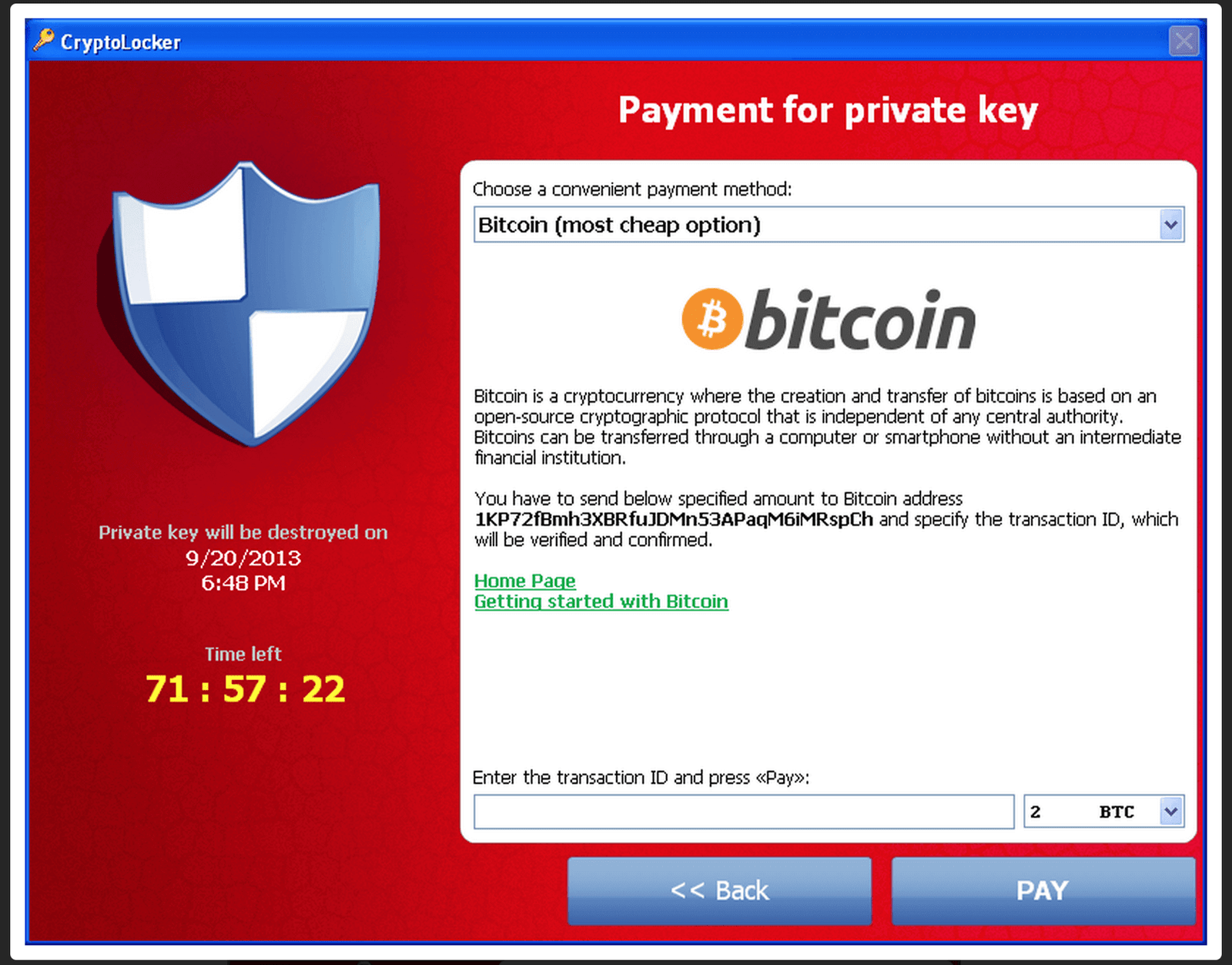
This ransomware attacks Windows users. It is known since 2013 and is the preliminary malware of Cryptolocker family. It attacks users via malicious email attachments. Once you click on malicious attachment, it starts encrypting files on your system and on your mounted device. This ransomware uses the RSA-2048 public key to target users. Once it completes encrypting files, the malware then displays a message on a system which offers users to decrypt the data if a certain payment is made. It uses bitcoin or a pre-paid cash voucher as a mode of payment.
KeRanger:

KeRanger ransomware is the first known real Mac ransomware, which is fully functional and is currently affecting users around the world. This malicious code was distributed from the official Transmission site with a different code signature. It was spread via Transmission version 2.9, which was later recalled. It uses phishing emails as it’s another vector. This malware was detected by the malware researcher firm, Palo Alto, early this year.
As have discussed, there have been some serious attempts to hack user’s data to ransom users. Though there are certain solutions that are available to prevent the effects of these malicious activities such as backup of data, keeping the system updated and others. Still many victims pay ransom to get rid of this headache. Let’s discuss certain reasons why you should not pay ransom to get away from this situation.
- You don’t alwaysget your data back: You need to understand here that ransomware attacks are initiated by people with a criminal mindset. Hence, there is no certainty of getting back the data even after making payment against it.
- It will increase these attacks: Once you pay ransom against your data, it will give a moral boost to these ransomware attackers. In such a case with monetary(ransom) assistance and with their criminal expertise, there are strong chances they will attack other users too.
- No assurity of data safety: Once you pay ransom to get your data back from an attacker, you will still be prone to this attack anytime soon. As the attacker now knows the importance of data for you.
- Data compromised: You are dealing with a criminal. There are strong possibilities that your data has been already been compromised.
- Be proactive: This should be the most valid point to safeguard your data against any ransom and a valid reason to not pay the ransom. Keep your system safe with the full gamut of security software – antivirus, anti-phishing, anti-spam, firewall and anything possible. This way you will be able to avert any ransomware attack to a larger extent.
Solution: Anti-malware programs are effective to some extent to prevent these ransomware threats. Using an anti-spam system is a good idea as most of the ransomware have been spread via spam email campaigns. You can also try for certain decryption tools as well for specific ransomware threats. Thus the simplest solution available to safeguard yourself from the negative effects of a ransomware attack is to keep a backup of all the data. As the decryption key to manyof these ransomware attacks is still unavailable, keeping a backup of your data proves to be a wise action. You can simply put the data backup on external drives or you can avail Cloud services for instant access to data.